Intelligent or interactive carpets, often referred to as SMART carpets, are advanced flooring solutions that incorporate technology to provide additional functionalities and interactivity. SMART carpets typically incorporate sensors, embedded electronics, and connectivity features to provide various functionalities.
While SMART carpets have been explored in different contexts, such as healthcare, sports, and home automation, their integration into retail environments is relatively limited. These carpets are designed to go beyond their traditional role of providing a comfortable and aesthetically pleasing flooring surface. Here are some key features and functionalities that intelligent or interactive carpets may offer:
- Sensors: SMART carpets can be equipped with various sensors embedded within the carpet fibers or beneath the surface. These sensors can detect different types of data, such as pressure, temperature, or movement. For example, pressure sensors can identify footfalls or track the presence of individuals on the carpet.
- Connectivity: SMART carpets often have built-in connectivity capabilities, allowing them to communicate with other devices or networks. This connectivity can be wired or wireless, enabling seamless integration with other smart systems and technologies.
- Data Analysis: The sensors embedded in SMART carpets collect data, which can be analyzed to gain insights and make informed decisions. For instance, by analyzing footfall patterns, retailers can understand customer behavior, optimize store layouts, and enhance customer experiences.
- Interactivity: SMART carpets can offer interactive features to engage users. They can incorporate touch-sensitive surfaces or even projection capabilities to display interactive content. Users can interact with the carpet by tapping, swiping, or stepping on designated areas, triggering responses or displaying information.
- Ambient Feedback: Intelligent carpets can provide ambient feedback based on user interactions or environmental factors. For example, they can change colors, patterns, or textures in response to touch or movement, creating dynamic and immersive experiences.
- Safety and Security: SMART carpets can contribute to safety and security measures. For instance, they can detect and alert staff to unauthorized movements or recognize potential hazards, such as spills or slippery surfaces.
- Energy Efficiency: Some SMART carpets incorporate energy-saving features. They can adjust lighting levels or temperature based on occupancy, optimizing energy consumption in retail or commercial spacess
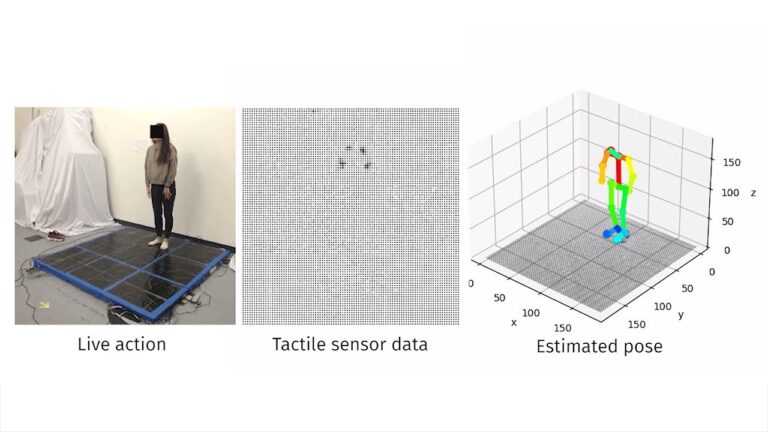
An Example Video on Smart Carpets created by MIT that estimate Estimate a person’s 3D pose using only tactile sensors. Although this is different use case than one under discussion in this article but still offers a visual perspective on the use of Smart Carpets.
It’s worth noting that the specific features and functionalities of intelligent or interactive carpets can vary depending on the manufacturer, application, and intended use. Advancements in technology may introduce new capabilities to further enhance the interactivity and intelligence of these carpets.
Intelligent or interactive carpets can potentially incorporate vacuuming capabilities to help keep the area underneath clean. While it is technically possible to integrate vacuuming mechanisms into SMART carpets, it’s important to note that such a feature would likely add complexity and cost to the product.
Here’s how a SMART carpet with built-in vacuuming functionality might work:
- Sensors: The carpet would be equipped with sensors to detect the presence of dirt or debris underneath the surface. These sensors could use various techniques such as optical sensors or ultrasonic sensors to identify areas that require cleaning.
- Vacuuming Mechanism: The SMART carpet would be designed with a vacuuming mechanism integrated into its structure. This mechanism could consist of small suction openings or channels strategically placed throughout the carpet.
- Cleaning Cycle: When the sensors detect a significant amount of dirt or debris, the vacuuming mechanism would be activated. It would generate suction, pulling in the dirt from underneath the carpet.
- Filtration System: The SMART carpet’s vacuuming mechanism would include a filtration system to capture and contain the collected dirt. This system could consist of filters that prevent the dirt from recirculating into the surrounding environment.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Periodically, the filtration system would need to be emptied or replaced to ensure the continued effectiveness of the vacuuming functionality. The SMART carpet might also require regular maintenance, such as cleaning or servicing of the vacuuming components.
Building a SMART carpet from scratch involves integrating various components such as sensors, connectivity, data analysis, interactivity, ambient feedback, safety and security, and energy efficiency. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the PSEUDO code (it is python based but written in simple language and can be modified to any programming language syntax) that could be used for creating a SMART carpet for home use, along with implementation code for each step:
import random
import time
#import important libraries like time and random to generate random data and perform time based functions - these are programming language based and syntax could be different
# Step 1: Initialize variables and constants
threshold = 0.5 # Threshold for triggering actions or feedback
dirt_threshold = 0.5 # Minimum amount of dirt to trigger vacuuming
vacuum_power = 0.8 # Power level of the vacuuming mechanism
# Step 2: Define data structures
carpet_data = {} # Dictionary to store carpet data
dirty_areas = [] # List to track dirty areas
# Step 3: Generate random sample data
def generate_sample_data():
# Your code to generate complex random sample data
# Populate carpet_data with dirt levels, location and carpet features
carpet_data['temperature'] = random.uniform(18, 25) # Simulated temperature data
carpet_data['pressure'] = random.uniform(0, 1) # Simulated pressure data
carpet_data['occupancy'] = random.choice([True, False]) # Simulated occupancy data
carpet_data['area1'] = {'dirt_level': random.uniform(0, 1)}
carpet_data['area2'] = {'dirt_level': random.uniform(0, 1)}
carpet_data['area3'] = {'dirt_level': random.uniform(0, 1)}
carpet_data['area4'] = {'dirt_level': random.uniform(0, 1)}
carpet_data['area5'] = {'dirt_level': random.uniform(0, 1)}
# Add more simulated data for other features
# Step 4: Main loop for continuous monitoring
while True:
# Step 5: Retrieve carpet data
def get_carpet_data():
generate_sample_data()
return carpet_data
# Step 6: Analyze carpet data
def analyze_data(data):
temperature = data['temperature']
pressure = data['pressure']
occupancy = data['occupancy']
# Perform desired data analysis tasks
if temperature > threshold:
# Take necessary action or trigger an alert
print("Temperature threshold exceeded!")
if pressure > threshold:
# Take necessary action or trigger an alert
print("Pressure threshold exceeded!")
if occupancy:
# Perform specific operations based on occupancy status
print("Carpet is occupied.")
# Step 7: Interact with users
def interact_with_users(data):
# Your code to enable interactivity with users
# Capture user interactions and trigger appropriate responses or actions
temperature = data['temperature']
occupancy = data['occupancy']
print("Interacting with users...")
# Example: Simulated user interaction
if temperature > 23:
# Adjust temperature settings based on user input
desired_temperature = input("It's getting warm. Would you like to adjust the temperature? ")
if desired_temperature:
# Adjust the temperature based on user preference
print("Adjusting temperature to", desired_temperature, "degrees.")
if occupancy:
# Perform specific operations based on user interactions
user_input = input("Welcome! How can I assist you today? ")
# Process user input and trigger appropriate actions
# Step 8: Provide ambient feedback
def provide_ambient_feedback(data):
# Your code to provide ambient feedback
# Adjust the carpet's visual or tactile features based on the carpet data
pressure = data['pressure']
occupancy = data['occupancy']
print("Providing ambient feedback...")
# Example: Simulated ambient feedback
if pressure > threshold:
# Adjust the carpet surface based on pressure sensors
print("Pressure sensors activated. Adjusting carpet surface.")
if occupancy:
# Activate specific ambient features when carpet is occupied
print("Carpet lights up to greet the user.")
# Step 9: Ensure safety and security
def ensure_safety_and_security(data):
# Your code to ensure safety and security
# Implement necessary safety and security features based on the carpet data
occupancy = data['occupancy']
print("Ensuring safety and security...")
# Example: Simulated safety feature
if occupancy:
# Check for any unauthorized activity when carpet is occupied
print("Occupancy detected. Checking for any unauthorized activity.")
else:
# Activate security measures when carpet is unoccupied
print("No occupancy detected. Activating security measures.")
# Step 10: Optimize energy efficiency
def optimize_energy_efficiency(data):
# Your code to optimize energy efficiency
# Adjust lighting levels, temperature, etc. based on the carpet data
temperature = data['temperature']
pressure = data['pressure']
print("Optimizing energy efficiency...")
# Example: Simulated energy optimization
if temperature > 24:
# Lower temperature settings to conserve energy when it's too high
print("Temperature is high. Lowering temp settings to conserve energy.")
if pressure > threshold:
# Turn off unnecessary lighting when pressure sensors are activated
print("Pressure sensors activated. Turning off unnecessary lighting.")
# Step 11: Vacuuming Dirty Areas function Check dirt levels and mark dirty areas
def check_dirty_areas(data):
dirty_threshold = 0.5 # Threshold for considering an area as dirty
dirty_areas = [] # List to track dirty areas
# Your code to check dirt levels and mark dirty areas
# Identify areas with dirt levels above the threshold
dirt_area1 = data['dirt_area1']
dirt_area2 = data['dirt_area2']
dirt_area3 = data['dirt_area3']
dirt_area4 = data['dirt_area4']
dirt_area5 = data['dirt_area5']
# Add more variables as needed
print("Checking dirt levels and marking dirty areas...")
# Example: Simulated dirty area detection
if dirt_area1 > dirty_threshold:
dirty_areas.append('area1')
if dirt_area2 > dirty_threshold:
dirty_areas.append('area2')
if dirt_area3 > dirty_threshold:
dirty_areas.append('area3')
if dirt_area4 > dirty_threshold:
dirty_areas.append('area4')
if dirt_area5 > dirty_threshold:
dirty_areas.append('area5')
# Add more dirty area checks based on other variables
# Vacuum dirty areas
def vacuum_area(area, power):
# Your code to activate the vacuuming mechanism with specified area & power level
print("Vacuuming area", area, "with power level", power)
# Simulated vacuuming process
time.sleep(2)
print("Area", area, "cleaned.")
NOW MAKE THE FUNCTION CALLS TO TRIGGER REQUIRED ACTIONS
# Step 12: Retrieve carpet data
carpet_data = get_carpet_data()
# Step 13: Analyze carpet data
analyze_data(carpet_data)
# Step 14: Interact with users
interact_with_users(carpet_data)
# Step 15: Provide ambient feedback
provide_ambient_feedback(carpet_data)
# Step 16: Ensure safety and security
ensure_safety_and_security(carpet_data)
# Step 17: Optimize energy efficiency
optimize_energy_efficiency(carpet_data)
# Step 18: Vacuum the carpet
if dirty_threshold > 0.5
vacuum(area, power)
# Step 19: Sleep/wait for the next iteration
time.sleep(1) #Adjust the sleep duration based on desired frequency of monitoring
Step by Step Explanation of the Code
- Step 1: Initializes variables and constants such as the threshold for triggering actions or feedback, dirt threshold for vacuuming, and vacuum power level.
- Step 2: Defines data structures:
carpet_data(a dictionary to store carpet data) anddirty_areas(a list to track dirty areas). - Step 3:
generate_sample_data()function generates random sample data for carpet features such as temperature, pressure, and occupancy levels. It populates thecarpet_datadictionary with these values. - Step 4: Starts a continuous loop for monitoring the carpet.
- Step 5:
get_carpet_data()function retrieves the latest carpet data by calling thegenerate_sample_data()function and returns the updatedcarpet_data. - Step 6:
analyze_data(data)function receives the carpet data as an argument and performs analysis tasks based on specific conditions. For example, it checks if the temperature or pressure exceeds the threshold and triggers the necessary actions or alerts. - Step 7:
interact_with_users(data)function enables interactivity with users. It captures user interactions and triggers appropriate responses or actions based on the carpet data. For instance, it adjusts temperature settings based on user input. - Step 8:
provide_ambient_feedback(data)function provides ambient feedback based on the carpet data. It adjusts the carpet’s visual or tactile features, such as adjusting the carpet surface based on pressure sensors or activating ambient features when the carpet is occupied. - Step 9:
ensure_safety_and_security(data)function ensures safety and security based on the carpet data. It implements necessary safety and security features, such as checking for un-authorized activity when the carpet is occupied or activating security measures when the carpet is unoccupied. - Step 10:
optimize_energy_efficiency(data)function optimizes energy efficiency based on the carpet data. It adjusts lighting levels, temperature settings, etc., to conserve energy. For example, it lowers temperature settings when it’s too high or turns off unnecessary lighting based on pressure sensor activation. - Step 11:
check_dirty_areas(data)function checks dirt levels and marks dirty areas on the carpet. It identifies areas with dirt levels above the threshold and appends them to thedirty_areaslist. - Step 12: Retrieves the latest carpet data by calling the
get_carpet_data()function and assigns it to thecarpet_datavariable. - Step 13: Calls the
analyze_data(carpet_data)function to analyze the carpet data and perform necessary actions or triggers based on the analysis. - Step 14: Calls the
interact_with_users(carpet_data)function to enable interaction with users based on the carpet data. - Step 15: Calls the
provide_ambient_feedback(carpet_data)function to provide ambient feedback based on the carpet data. - Step 16: Calls the
ensure_safety_and_security(carpet_data)function to ensure safety and security based on the carpet data. - Step 17: Calls the
optimize_energy_efficiency(carpet_data)function to optimize energy efficiency based on the carpet data. - Step 18: If the dirt threshold on the carpet exceeds the specified threshold value, it calls the
vacuum(area, power)function to initiate the vacuuming process with required area to vacuum with desired power value. - Step 19: Sleeps for a specified duration before the next iteration of the monitoring loop.
In conclusion, the software code behind smart carpets plays a pivotal role in transforming ordinary flooring into intelligent and interactive surfaces. We have explored the fundamental aspects of this code, including sensors, connectivity, data analysis, interactivity, ambient feedback, safety measures, and energy efficiency.
By harnessing the power of complex random sample simulated data, smart carpets can adapt to changing conditions, provide valuable insights through data analysis, and interact seamlessly with users. The implementation code we discussed demonstrates how various variables and functions can be incorporated to optimize the carpet’s performance.
As technology continues to evolve, smart carpets are poised to revolutionize our living spaces, offering a dynamic and personalized experience. From ensuring cleanliness with automated vacuuming to providing ambient feedback based on environmental factors, these carpets exemplify the intersection of software and innovation. The possibilities for smart carpets are vast, with potential applications ranging from homes and offices to healthcare facilities and public spaces. As we continue to unlock the potential of intelligent flooring, it is an exciting time to witness the transformative impact of software code on our everyday lives.
In the coming years, we can anticipate further advancements in the software code of smart carpets, leading to even smarter and more sophisticated features. With ongoing research and development, we can expect these innovative floorings to enhance our comfort, safety, and overall well-being. In essence, the software code behind smart carpets unveils a world of possibilities, where our floors become intelligent companions that adapt, engage, and create a truly immersive environment.